The terms “net income” and “net profit” are frequently used synonymously in the context of business. But there is a significant distinction between the Net Income and Net Profit. While net profit is the sum of a firm’s remaining funds after all costs have been met, Net Income is the total amount of money a company has made during a specific period. Thus you must have got an idea of Net Income and Net Profit.
Let’s examine more closely to better grasp the distinction between Net Income and Net Profit.
Take-home Income: What Is It?
The total amount of money a business has made during a certain period is its take-home income (NI). This covers all sales revenue, interest income, investment income, and any other kinds of Income. When all Revenue has been totalled, Any costs are deducted before adding them up. The business is left with its take-home income as a result.
Sales are subtracted from the cost of products supplied, selling, general expenditures, capital expenditures, amortization, debt, tax, and other expenses to arrive at Net Income (NI), also known as net earnings. Investors can use this figure to determine how much a company’s Revenue exceeds its costs. This figure is a measure of a bank’s earnings and may be found on the income statement.
Key Lessons To Consider About Net Earnings(NI)
- Revenues with fewer costs, taxes, and interest equal net earnings (NI).
- Net earnings are used to compute earnings per share.
- Because costs can be concealed via accounting techniques or revenues can be artificially overstated, investors should carefully examine the data used to calculate net earnings.
In addition, after deducting taxes and deductions from gross income, net earnings is a person’s Total Income or pre-tax Income.
Now let us look into the difference between wages after taxes and gross profit by understanding gross profit first.
Net Profit: What Exactly Is It?

The money a business has left over after all costs have been covered is known as net profit. This covers costs such as operating costs, taxes, and the cost of goods sold. The business’s net profit remains after all costs have been removed from gross Revenue.
Net profit, which is identical to Net Income, is the sum of a company’s earnings after deducting all costs. The costs of routine business operations, as well as amortization and taxes, are deducted from the total. A company’s gross profit, also known as its “bottom line,” is a reliable predictor of its profitability.
Although the fundamental meaning of gross profit is similar to that of net earnings, there are some differences in how they are used by different businesses. In order to distinguish between items taking account while excluding taxes while maintaining consistency in terms, “gross profit” may have seemed on a financial report in the context of “net profit after taxes” because the general term “profit” is calculated at various stages in a company’s financial reportage with varying qualifiers.
To ascertain, adhere to this Calculating Gross Profit:
Total Revenue – (Income Tax expense + Tax + Depreciation) = Gross Profit.
What Separates Net Earnings from Net Profit?
The primary distinction between net earnings and net profit is the inclusion of all sources of Income in net earnings, as opposed to net profit, which only includes sources of Income once all expenses have been met. Accordingly, net Profit is never higher than net Income. Let’s say, for illustration, that a business has a net revenue of $100,000. This signifies that they received $100,000 in total Income from all sources. However, after paying all costs, the business only has a net income of $50,000. The distinction between net earnings and gross Profit is as follows.
Net Profit: Why Is It Important?
An important sign of a firm’s financial well-being is net profit. It displays however much money the business still has after all costs have been met, and the remaining funds can be paid to shareholders or reinvested in the company. The amount of taxes owed by a business is also determined using net profit. As a result, businesses must monitor their net profit and make sure they are earning enough money to pay their bills and pay taxes.
How to Determine Net Profit
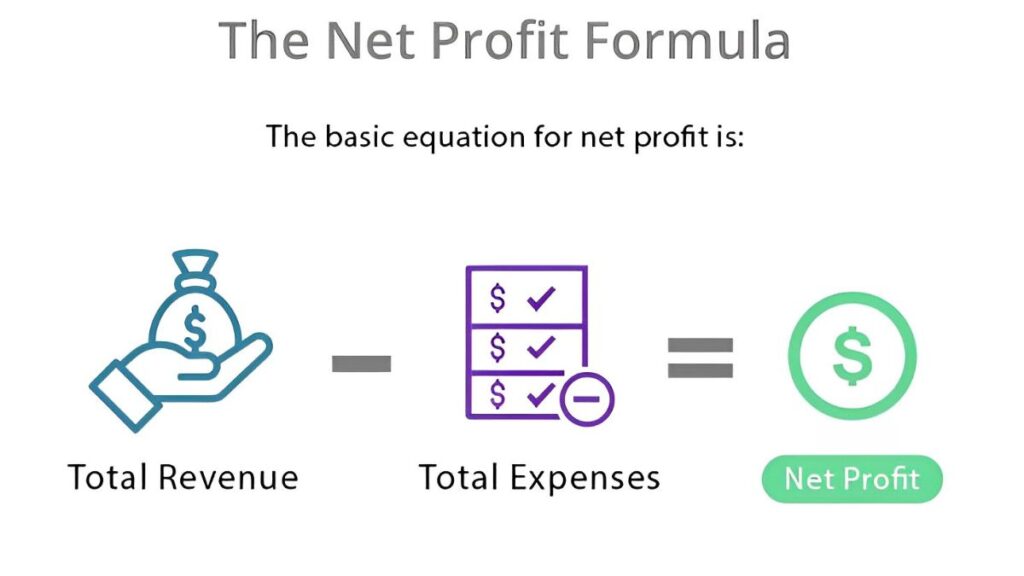
Calculating Net Income and Net Profit are very comparable. To start, total up all the company’s revenue sources. Purchases, interest, and investments are included in this. You must deduct any expenditures from the total Income once you obtain it. Contrary to net income, you just need to deduct costs associated with sales costs, operational costs, and taxes. The resultant figure represents the business’s Net Profit.
Illustration of Net Profit
Let’s now examine a net profit example. For the year, Company Xyz has the following revenues and costs:
Sales: $1,000,000
Expenses: $10,000
Contributions: $5,000
$5000 was the cost of the sold products.
Running costs: $200,000.
Taxes: $100,000
We must add up all of the Revenue and deduct all of the cost of products sold, operational costs, and tax expenses to get the company’s net Profit. This results in a $5,000 net profit ($1,000,000 plus $10,000 plus $5,000 – $2.3 thousand – ($200,000 – $100,000).
How To Calculate Net Pay (Income)
The calculation of Net Pay is not difficult. To start, total up all the company’s revenue sources. Sales, Income, and investments are included in this. You must deduct any expenditures from the Total Income once you obtain it. This covers costs such as operating costs, taxes, and the cost of goods sold. The outcome is the business’s Net Pay.
Illustration of Net Pay
Let us just look at a scenario to clarify Net Pay. For the year, Company Xyz has the following revenues and costs:
Sales: $1,000,000
Expenses: $10,000
Contributions: $5,000
$5000 was the cost of the sold products.
Running costs: $200,000.
Taxes: $100,000
To determine the business’s Net Pay, we must add up each of the earnings and deduct all of the outgoing costs. As a result, we have a net revenue of $305k ($1m + 10k + 5k – 500k – 200k – 100k).
Final Reflections
As you’ll see, the variance in net income is substantial. While net income only includes money after all expenses are paid, net Income covers all sources of Income. The calculation of a firm’s tax liability is based on net Profit, a fundamental sign of its financial health. As a result, businesses must monitor their net Profit to make sure they are earning enough money to pay their bills and pay taxes.
One kind of Profit is net Income. After subtracting all expenses, it is commonly referred to as the “bottom line” amount for small enterprises on their income statement. On the other hand, net Profit is a little unique as it is extremely profitable that a company makes after deducting several categories of expenses. The firm’s tax obligation on its Income, as well as its business profitability, is determined using net Profit.
There isn’t a magic number. A healthy sales revenue depends on the company’s operations and the sector it serves. You can use the industry median net income as a comparison when comparing your net Profit. Net Profit may also be impacted by the economy. We might state that a healthy net profit margin surpasses 10% in general.
Net Income is the “bottom line” of the company’s balance sheet from which all expenditures have been subtracted, making this the distinction between net earnings and economic profits that is most immediately apparent. However, net Profit reveals the company’s profitability over a specified time frame.
For more insights and ideas related to businesses, marketing, social media, financial awareness, business essentials and technology check out BiznessHub, to explore further opportunities and knowledge.
FAQs
Ques. What is the difference between Net Income and Net Profit?
Ans. The basic difference between Net Income and Net Profit is that net Income is basic Income after all the expenses, while net Profit is the total Profit earned after deducting all the expenses.
Ques. How is net Profit useful?
Ans. It aids in calculating the earnings we get per share.
Ques. How is net Income useful?
Ans. It solely tells about the Profit of the organization.




